|
|
The immune system is complex and relies on many nutrients. As a topic central to the functioning of the immune system, we discuss how vitamin C is crucial to your immune system. The mechanisms by which your immune system uses vitamin C are well understood.
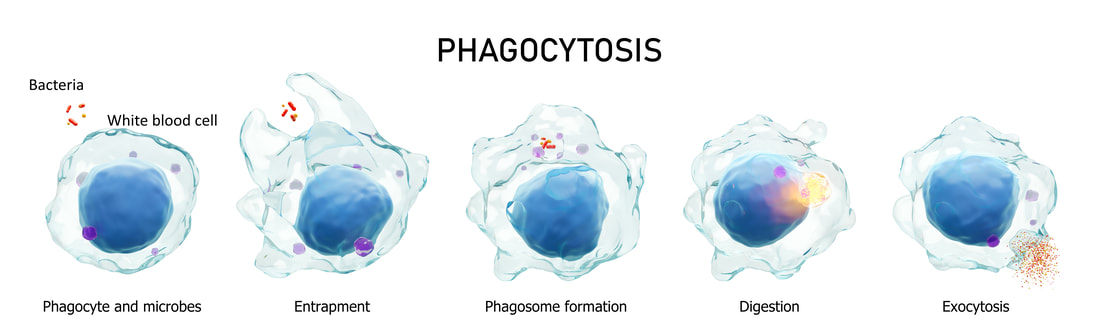
The first of these mechanisms relates to phagocytes (which are types of white blood cell), which are present throughout the body, including the blood and lymph systems, and increase in number when the body is fighting infection and disease. Your phagocytes protect you against infection by literally consuming foreign harmful invaders such as bacteria and viruses (in a process called phagocytosis). This is good for you, but not so good for the phagocytes, which require restoration to continue their fight against the infection. This restoration is achieved by the phagocytes accumulating vitamin C in high concentrations. Specifically, the phagocytes actively accumulate vitamin C to concentrations that are 50 to 100 times blood plasma concentrations. Such high concentrations of vitamin C protect the phagocytes from oxidative damage, regenerate glutathione and vitamin E in the phagocytes, and modulate the immune function of the phagocytes.
Essentially, vitamin C protects and optimizes white blood cells in their fight against infections, bacteria and viruses.
In our view, it is disturbing that this simple, well-understood functioning of the human immune system has not been explained to the general public by health authorities around the world. Vitamin C is further important to immunity in that it protects molecules and cell structures from free radicals and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, and improves the integrity of the skin. The importance of vitamin C to good health Lower vitamin C levels are associated with higher incidences of cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cataracts and age-related macular degeneration, and possibly neurode-generative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Vitamin C decreases systemic inflammation and reduces fatigue. In the most general sense of good health, vitamin C is involved in dozens of essential physiological processes. Examples are the synthesis of lipids/proteins; the synthesis of neuromodulators and neurotransmitters; the metabolism of cholesterol, carbohydrate, and protein; and cellular respiration. Vitamin C is used in making eight enzymes that are responsible for collagen hydroxylation, hormone and amino acid biosynthesis, and the biosynthesis of carnitine, which is a molecule required in the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria to generate metabolic energy. The body cannot function optimally without good levels of vitamin C. |
|